Could An Ear Infection Cause Neck Pain? Find The Truth!
Curious if an ear infection could be the source of your neck pain? Dive into the potential correlation between these two conditions, their symptoms, and how to manage them effectively. Gain insights into how ear infections may trigger neck discomfort and when to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Empower yourself with knowledge to address both ear infections and associated neck pain for improved well-being.

Disclaimer: Our recommendations are sincere, driven by the products’ benefits. When you buy through our links, we may earn a commission, backing our testing and development at no extra cost to you.
Ear infections are a common ailment that can cause a range of uncomfortable symptoms, from earache and fever to difficulty hearing. However, one lesser-known symptom that often leaves people perplexed is neck pain. While it may seem unrelated, an ear infection can indeed lead to discomfort and stiffness in the neck area. In this article, we’ll explore the connection between ear infections and neck pain, delving into the causes, symptoms, and potential remedies.
The Anatomy Of Ear And Neck Connections
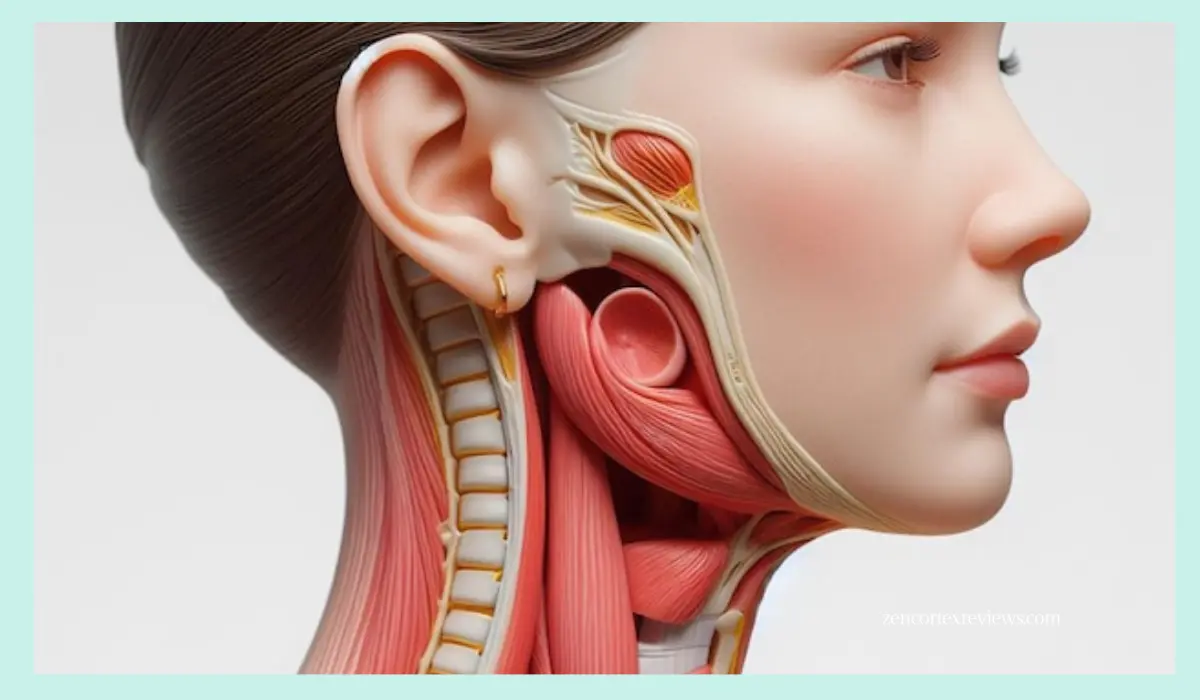
To understand the link between ear infections and neck pain, it’s essential to examine the intricate anatomy of the ear and its surrounding structures. The ear is a complex organ that comprises three main parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. The middle ear, in particular, plays a crucial role in this connection.
The middle ear is a small air-filled cavity that houses three tiny bones called ossicles: the malleus, incus, and stapes. These bones are responsible for transmitting sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. Additionally, the middle ear is connected to the throat through a narrow channel called the Eustachian tube, which helps regulate air pressure and drain excess fluid from the ear.
When an infection occurs in the middle ear, it can lead to inflammation and buildup of fluid or pus. This pressure and swelling can potentially spread to nearby structures, including the muscles and tissues surrounding the neck area.
Types Of Ear Infections And Their Connection To Neck Pain
Several types of ear infections can contribute to neck pain:
1. Acute Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection)
This is the most common type of ear infection, particularly in children. It occurs when the middle ear becomes inflamed due to a viral or bacterial infection. As the infection progresses, the buildup of fluid and pressure can cause pain and discomfort that radiates to the neck and surrounding areas.
2. Otitis Externa (Swimmer’s Ear)
Also known as swimmer’s ear, this infection affects the outer ear canal. While it may not directly cause neck pain, the swelling and inflammation can potentially spread to the surrounding tissues and muscles, leading to discomfort and stiffness in the neck region.
3. Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis is a rare but serious complication of an untreated middle ear infection. It occurs when the infection spreads to the mastoid bone, located behind the ear. This condition can cause severe neck pain, swelling, and tenderness due to the proximity of the affected area to the neck muscles and lymph nodes.
Symptoms Of Neck Pain Associated With Ear Infections
In addition to the typical symptoms of an ear infection, such as earache, fever, and hearing difficulties, individuals may experience the following neck-related symptoms:
- Neck stiffness and reduced mobility
- Tenderness or pain when moving the neck
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck area
- Radiating pain from the ear to the neck and shoulder region
- Headaches or migraines due to muscle tension in the neck
It’s important to note that the severity of neck pain can vary depending on the type and severity of the ear infection, as well as individual factors such as age and overall health.
Diagnosis And Treatment
If you suspect that your neck pain is related to an ear infection, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Your healthcare provider will likely perform the following steps to diagnose and treat the underlying condition:
❇️Physical examination: Your doctor will examine your ears, neck, and throat to look for signs of infection or inflammation.
❇️Imaging tests: In some cases, a CT scan or MRI may be ordered to evaluate the extent of the infection and rule out other potential causes of neck pain.
❇️Antibiotic treatment: If a bacterial infection is present, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to help clear the infection and reduce inflammation.
❇️Pain management: Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications may be recommended to alleviate discomfort and reduce swelling.
❇️Drainage: In severe cases, surgical drainage of fluid or pus from the middle ear may be necessary to relieve pressure and prevent complications.
Home Remedies And Self-Care Strategies
While professional medical treatment is essential for resolving an ear infection and associated neck pain, there are several home remedies and self-care strategies that can provide relief and support the healing process:
❇️Warm compresses: Applying a warm, moist compress to the affected ear and neck area can help reduce pain and promote drainage.
❇️Over-the-counter pain relievers: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate pain and inflammation.
❇️Rest and hydration: Getting plenty of rest and staying hydrated can support the body’s healing processes and reduce overall discomfort.
❇️Neck stretches and exercises: Gentle neck stretches and exercises can help alleviate muscle tension and improve mobility, but it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before attempting any new exercises.
Prevention And Precautions
While ear infections can sometimes be unavoidable, there are several preventive measures you can take to reduce your risk:
❇️Practice good hygiene: Regularly washing your hands and avoiding touching or inserting objects into your ears can help prevent the spread of bacteria and infections.
❇️Manage allergies and respiratory infections: Keeping allergies and respiratory conditions under control can help prevent complications that may lead to ear infections.
❇️Avoid exposure to loud noises: Excessive noise can damage the delicate structures of the ear and increase the risk of infections.
❇️Seek prompt treatment: If you suspect an ear infection, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly to prevent the infection from spreading or causing complications like neck pain.
Sum Up
While ear infections and neck pain may seem unrelated at first glance, the intricate connections between the ear and surrounding structures can lead to this uncomfortable combination of symptoms. By understanding the potential causes, recognizing the signs, and seeking proper medical treatment, individuals can effectively manage both the ear infection and associated neck pain. Remember, prompt attention and adherence to recommended treatments are key to resolving the issue and preventing further complications.
References
Lindsay Martinez
Lindsay Martinez, Au.D., is a licensed audiologist with over 10 years of experience in the field of hearing healthcare. She earned her Doctor of Audiology degree from the University of California, Los Angeles, and currently practices at Martinez Hearing Clinic, a leading audiology practice in the San Francisco Bay Area. As an expert in diagnosing and treating a wide range of hearing disorders, Dr. Martinez specializes in fitting advanced hearing aids and assistive listening devices. She is a fellow of the American Academy of Audiology and has published numerous peer-reviewed articles on topics such as noise-induced hearing loss and the latest innovations in hearing technology. Passionate about patient education, Dr. Martinez is committed to helping her patients improve their hearing and overall quality of life.
